Alo Yeditepe
Alo Yeditepe
What is Broken Heart Syndrome? Symptoms and Treatment
Although intense emotional traumas lead to heartbreak, they can actually have significant physical effects on the heart. Cardiology Specialist Prof.Dr. Ali BUTURAK stated that sudden intense sadness, disappointment and stress can lead to broken heart syndrome. Dr. Ali Buturak said that the patient may experience complaints such as sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, dizziness and fainting.
Dr. Buturak said that the disease is triggered by sudden psychological traumas such as losing a spouse, lover or first-degree relative or a loved one, heavy emotional situations such as separation after a long-term relationship, divorce or being cheated on, or receiving news that will shake the person deeply. He emphasized that the danger of drowning, natural disasters such as earthquakes and some physical traumas can also cause broken heart syndrome.
What is Broken Heart Syndrome?
Broken heart syndrome is a special condition characterized by a sudden contraction defect in part or all of the heart muscle, usually following a severe emotional or physical stress. The main function of the heart muscle is to pump and send blood to other organs and tissues of the body. When the heart muscle cannot contract sufficiently and cannot fully fulfill its duty, life-threatening situations may develop.
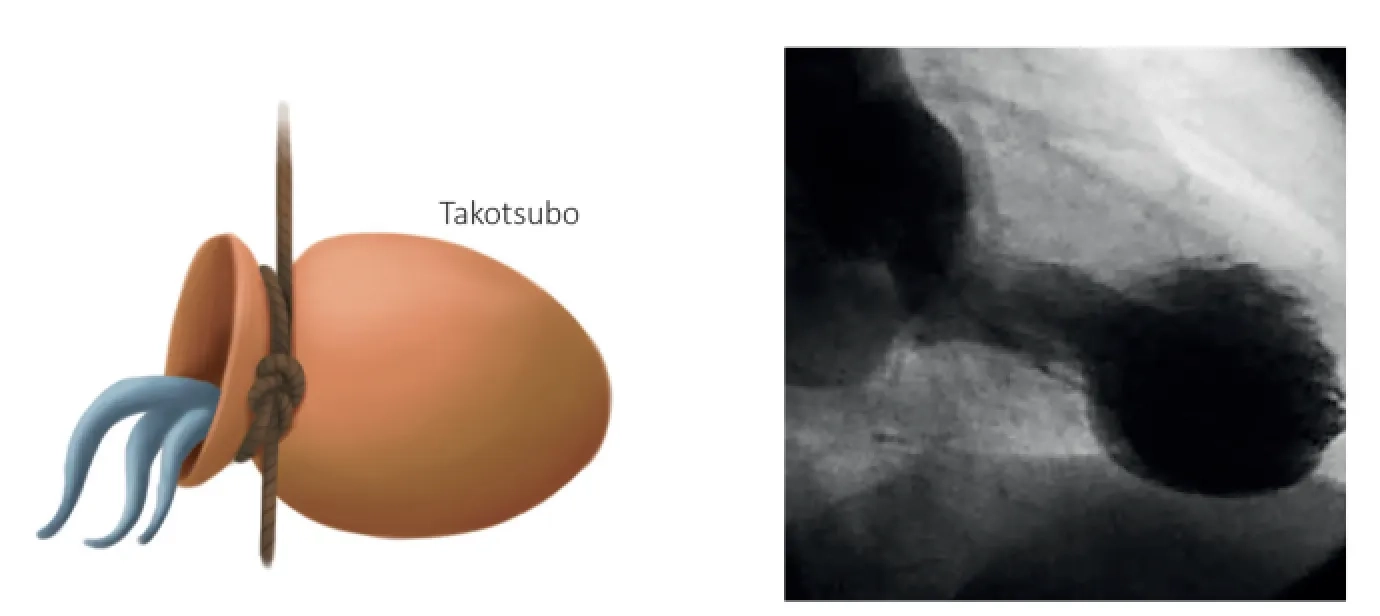
This disease, which was first described as Takotsubo Syndrome in Japan in 1990, was given this name because the Japanese cardiologist who described the disease compared the images of the affected heart muscle to Takotsubo, a vase-like tool used by the Japanese to hunt octopuses, with a narrow mouth and a wide base. ???(Figure 1. Takotsubo). However, in almost all of the cases reported in the following period, it was observed that there was a triggering situation that would cause severe sadness or stress just before the sudden onset of this disease, and the disease began to be called stress cardiomyopathy or broken heart syndrome.
What are the symptoms of Broken Heart Syndrome?
Sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, dizziness and fainting are the main symptoms. All patients who have these complaints and who have experienced psychological or physical stress, especially in the last 1-5 days, should immediately contact the emergency department of the nearest hospital. Especially sudden onset of chest pain causes it to be confused with a heart attack. The signs and symptoms are almost exactly similar to a heart attack.
What Causes Broken Heart Syndrome?
As a result of the excessive activity of some regions in the brain after sudden intense sadness, disappointment or stress, there is an increase in the stress hormone levels in the blood to levels that can cause damage to the tissues. These hormones attack the heart muscle and small capillaries of the heart, causing sudden contraction defects in the heart muscle and loss of function in small vessels, disrupting cardiovascular circulation.
What are the Factors That Trigger Broken Heart Syndrome?
The triggering factor is often the loss of a loved one (spouse, lover or the news of the death of a first-degree relative), heavy emotional situations such as separation (divorce) or cheating after a long-term relationship, or receiving news that will shake the person deeply (learning that he/she has cancer, etc.). There may be sudden psychological traumas such as In addition, negative experiences experienced by the person (danger of drowning, earthquake damage, etc.) and some physical traumas can also cause broken heart syndrome.
How is Broken Heart Syndrome Diagnosed?
In patients in whom broken heart syndrome is suspected by the cardiologist; blood tests (blood tests that show heart muscle damage), electrocardiography, echocardiography, telecardiography and coronary angiography are performed.
How Is Broken Heart Syndrome Treated?
Although the condition is mostly benign and resolves spontaneously, every diagnosed patient is hospitalized and treated. In the coronary angiography of these patients, the coronary arteries are normal, but since the problem is damage to the heart muscle that causes a contraction defect, the patients suffer from heart failure, life-threatening rhythm disorders and other complications (fainting, clots from the heart to the brain and other regions, etc.) that will occur as a result of this damage. They should be followed closely and receive treatment. If the patient has signs of heart failure, drug treatment must be started. Conditions such as arrhythmia or intracardiac clot formation should be treated as necessary and the patient supported.
Frequently Asked Questions About Broken Heart Syndrome
What is the Frequency of Broken Heart Syndrome?
Although its frequency is not known exactly, it is known that it is 15-30 cases/100000 per year and the actual diagnosis is Broken Heart Syndrome in 2-3% of patients whose preliminary diagnosis is heart attack.
Its frequency is higher in women (5-6% of heart attack cases) and is mostly seen after the age of 50 - especially after menopause.
How is Broken Heart Syndrome Different from a Heart Attack?
Heart muscle damage that occurs after a heart attack does not heal spontaneously and often leaves permanent damage to patients. However, heart muscle dysfunction in Broken Heart Syndrome usually resolves spontaneously within a few weeks. A second difference is that the condition responsible for a heart attack is stenosis and occlusion of the heart vessels, whereas in broken heart syndrome, there is no serious stenosis or occlusion in the heart vessels.
Is the problem in Broken Heart Syndrome temporary? Does it cause permanent problems in the heart?
Heart muscle damage is temporary in many patients, and the contraction and relaxation functions of the heart usually recover completely after a few weeks from the onset. However, very rarely (<1% of patients) it may cause permanent damage. The most important point here is that patients receive appropriate treatment and support as soon as they are diagnosed.
Can Broken Heart Syndrome be prevented?
There is no known treatment to prevent broken heart syndrome. But learning stress management and problem-solving techniques can help you limit physical and emotional stress. It may be helpful to practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, journaling or mindfulness, taking a hot bath, lighting scented candles, taking long deep breaths and exhaling slowly. Depending on the source of your stress, joining a support group or a professional counselor to talk about your stress and share coping skills may also be helpful for stress management.
Additionally, adopting healthy habits can help manage physical or emotional stress; Such as gaining a healthy eating habit such as the Mediterranean diet, exercising regularly (30 minutes at least five times a week), getting enough sleep (7-9 hours a night), socializing, and avoiding the use of tobacco and tobacco products.
This content was prepared by Yeditepe University Hospitals Medical Editorial Board.
”
See Also
- What is Heart Rhythm Disorder (Arrhythmia)? Symptoms and Causes
- How Do We Know When We Have a Heart Attack?
- What is Sudden Cardiac Death? What are the Symptoms?
- Risk Factors in Heart Diseases
- Heart Valve Diseases and Treatment Methods
- How Do Heart Disease Risk Factors Affect Women and Men?
- What is a Heart Attack? What are the Symptoms of a Heart Attack?
- Carotid Artery Disease
- What is Renal Denervation?
- What is Intravenous Ultrasound (IVUS)?
- Renal Denervation in Hypertension Treatment
- What is TAVI?
- Is Your Heart Ready For Winter?
- The Risk of High Blood Pressure Increases as You Go to High Altitudes
- By 2025, Hypertension Patients Are Expected to Reach 1.5 Billion
- Misconceptions about the Female Heart
- Blood Pressure Holter
- Coronary CT Angiography (Virtual Angiography)
- Effort Test
- Heart Attack Causes and Symptoms
Alo Yeditepe







