Alo Yeditepe
Alo Yeditepe
Interventional Methods in the Treatment of Acute Stroke
What is Acute Stroke?
Acute stroke is a sudden dysfunction that occurs when the blood flow to the brain is cut off or decreased, as a result of the brain cells being deprived of oxygen and not being fed. It is also known as "paralysis".
What is the Incidence of Acute Stroke, and Why Is It Important?
Every year, approximately 200.000 acute stroke cases are seen in our country. Stroke ranks 3rd among the causes of death in our country and all over the world, and if the person survives an acute stroke, this causes long-term disability and dependency. Acute stroke is the most important cause of disability in the adult population.
Who Is at Risk for Acute Stroke, Is There a Distinction Between Men and Women? Is Age a Factor?
Those with poor nutrition, such as those who eat diets rich in saturated fat, physically inactive people, those who do not sleep regularly, smokers, patients with obesity, patients with uncontrolled diabetes and high blood pressure, patients with arrhythmias in the heart such as atrial fibrillation, patients having atherosclerosis or vessel stiffness with high cholesterol values are at risk. There is no clear difference in incidence for people, but when the literature is reviewed, it is observed that it is slightly more common in women. The risk of acute stroke increases with age, regardless of being male or female.
What is the Most Important Element in the Treatment of Acute Stroke?
The most important and life-saving, disability-preventing factor in the treatment of acute stroke is time. The earlier the intervention is made in acute stroke, the more satisfactory the treatment results will be. For this reason, as soon as the person or his/her relatives think or understand that he/she has an acute stroke, they should quickly transport him/her to a hospital that is capable of treating a stroke.
What Are the Signs of Acute Stroke?
The signs of acute stroke appear suddenly, in parallel with the reduction or cessation of cerebral blood flow. Unilateral facial shift, temporary visual disturbances, sudden unilateral vision, sudden weakness in the arms and legs, weakness and immobility, the sudden inability to speak, speech disorder, or slurring of the tongue are the symptoms of acute stroke. To make it easier to notice, tell the person to smile if you think there is a shift in the face, ask him/her to raise both arms in the air if you think there is weakness in the arms, and make him/her repeat a sentence you said if you think his/her speech is impaired.
Can the Symptoms of Acute Stroke Be Confused with Other Diseases?
It is possible that the symptoms can be confused with different diseases, but if you are experiencing any of the symptoms of acute stroke, you should definitely apply to a hospital that is capable of treating a stroke.
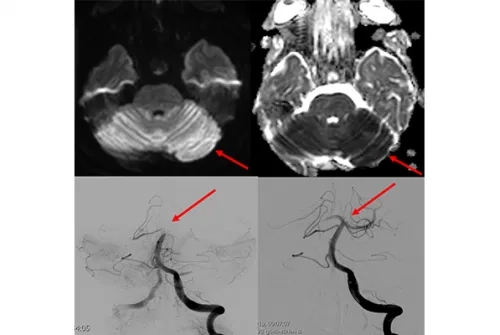
What Are the Indications for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke?
If stroke symptoms have not gone away for more than 6 hours, and if a blockage is detected in one of the main arteries in the brain, interventional radiology comes into play at this point. In the angiography unit, small pipes (catheters) are placed to the clot in the occluded artery in the brain by entering through the groin or the wrist, and the clot is mechanically removed and the blood flow in the occluded artery is restored to normal. When we look at the literature, it has been shown that mechanical removal of the clot, even in periods up to 6-24 hours after the emergence of stroke symptoms, allows the patient to continue his/her life independently or less dependently.
How Long Has Acute Stroke Treatment Been Applied in Interventional Radiology?
In interventional radiology, acute stroke treatment and mechanical removal of the clot have been applied for about 15-20 years.
What Are the Benefits of Acute Stroke Treatment for the Patient?
If the acute stroke is treated early, it becomes possible for patients to continue their lives without any disability or addiction. Some of our patients who come with sudden paralysis and speech disorders start to move their arms and legs after the clot is removed while they are still on the angiogram table, and their speech improves, they ask us questions, answer our questions, and return to work within a few days. These situations and moments we encounter in treatment are really pleasing.
Is There a Risk of Recurrence of Acute Stroke? In This Case, Can Interventional Methods Be Applied Again?
If the stroke risk factors that we mentioned at the beginning cannot be controlled and if these risky conditions are not improved, unfortunately, acute stroke may recur. When we encounter such a situation, that is, in a recurrent acute stroke patient, clot removal with interventional radiology can be applied again and there is no restriction.
Acute stroke treatment with interventional radiology is indeed a very important medical emergency in the prevention of disability, dependency, death, and loss of workforce in the adult population in our country and all over the world. Acute stroke and the adverse medical and socioeconomic consequences of acute stroke are all preventable.
This content was prepared by Yeditepe University Hospitals Medical Editorial Board.
”
See Also
- Radioembolization in Liver Tumor Treatment
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Stroke
- The Cause of Abdominal Pain Has Not Been Found for Years... Varicose Veins Appeared in Her Ovary
- Interventional Radiology is Used in Many Fields
- What Diseases Is Interventional Radiology Used For?
- What is a Brain Aneurysm?
Alo Yeditepe