Alo Yeditepe
Alo Yeditepe
Surgical Treatment of Pituitary Diseases
Surgical treatment remains in the first place in a significant proportion of pituitary tumors. It is possible to get rid of the disease completely with an expert and experienced surgical team and sufficient technological infrastructure. In the preparation process for surgery; detailed radiological imaging (3-Tesla MR, CT, etc.), a laboratory with the capacity to perform hormone examinations, and evaluation of the patient by a team consisting of neuro-ophthalmologist, neuro-radiologist, endocrinologist, and anesthesiologist who will examine the preoperative conditions of the patients in detail constitute the most important step.
Objectives of Surgical Treatment
● To determine the histopathological diagnosis of the lesion
● To eliminate the pressure effect on the important tissues around (the nerves responsible for the vision and eye movements)
● To remove the entire lesion when possible
● To maintain normal pituitary tissue
● To provide relief of preoperative symptoms
Surgical Treatment Options in Pituitary Diseases
The methods commonly used in the surgical treatment of pituitary lesions are as follows:
Transsphenoidal Surgery
Under general anesthesia, it is the removal of the lesions with the help of a microscope or endoscope by entering through the nose and opening a bone window at the base of the skull to reach the pituitary lesions. This type of surgery is widely used and is mostly preferred in small lesions. Other surgical treatment options are evaluated in areas that are difficult to reach with transsphenoidal surgery or may be at risk with transsphenoidal surgery.
Transcranial Surgery
It is to reach the lesion by opening a bone window in the skull and to remove the lesion with the help of a microscope. Craniotomy surgery is especially preferred in large lesions and lesions that cannot be completely reached by the transsphenoidal pathway.
In determining the type of surgery, many factors such as the size of the lesion, its relationship with the surrounding tissues, the type of lesion, and the physical structure of the patient (nasal anatomical structure) are evaluated and decided. All methods can be successfully applied by experienced surgeons at Yeditepe University Kosuyolu Hospital.
Factors Affecting the Success of Surgical Treatment in Pituitary Tumors
● Experience of the surgical team,
● Having sufficient technological infrastructure,
● Having advanced technology imaging devices (3-Tesla MR, CT, HD Neuroendoscopy, Intraoperative MRI, Neuronavigation, Intraoperative Ultrasound ),
● Operating rooms equipped with advanced technology (Intraoperative MRI, Intraoperative Ultrasound, Neuronavigation, HD Neuroendoscopy),
The patient was evaluated in detail by a team consisting of an endocrinologist, neuro-radiologist, neuro-pathologist, neuro-ophthalmologist, radiation oncologist, and anesthesiologist before the surgery.
In Which Patients Should Surgery Be Prioritized?
● Pituitary Apoplexy = Sudden bleeding in pituitary tumors,
● Large tumors that press on the eye nerve and cause vision problems in the patient,
● Cases that affect the hormonal balance and functioning of the body by secreting excessive hormones; cases that do not respond to drug therapy,
● Recurrent cases after surgery,
● Cases that cannot be diagnosed despite all examinations and tests,
● Drug-resistant cases.
Surgical Treatments Applied in Pituitary Diseases Clinic
The cases with the pituitary disease are presented to the council in the clinic formed by experienced experts in the field of Yeditepe University Kosuyolu Hospital. Patients who are decided to undergo surgical treatment by a council decision are examined in detail by an endocrinologist, neuroradiologist, neuro-ophthalmologist, neuro anesthesiologist, and neurosurgeon before surgery.
The patient is admitted to the clinic following the necessary preparations for anesthesia. Consent is obtained by informing the patient and their relatives about the technique of surgical treatment, type of intervention, risks, postoperative process, and alternative treatment methods.
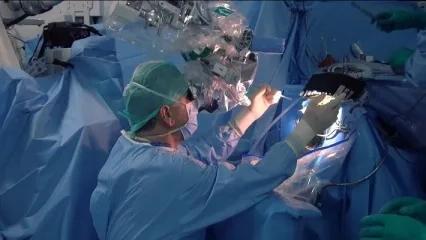
In our clinic, the Transsphenoidal Approach is most commonly used in the surgical treatment of pituitary tumors with endoscope-assisted Microneurosurgery. The radical removal of the tumors is aimed, and the following advanced technological devices are used in combination for this purpose.
Surgical Microscope: It allows the surgery to be performed in a smaller area by touching the normal tissue less in neurosurgery operations by using appropriate microsurgical techniques. Thanks to the surgical microscope, the surgeon can see the operation area much better by using smaller instruments, so it can work more safely. In addition to creating a safe treatment option for the patient, it normally provides the opportunity to perform operations with smaller incisions and thus reduces the time of discharge and return to the daily life of the patient.
Microsurgery requires a microscope that provides focusing and magnification at different depths, microsurgical instruments suitable for working under a microscope, and most importantly, experience in this field. In our hospital, pituitary tumors can be treated by entering through the nose in appropriate cases with up-to-date technologically equipped surgical microscopes.
Neuroendoscopy: It is an auxiliary tool frequently used in micro neurosurgery that contributes to the diagnosis and treatment of brain lesions under HD or 4K camera images. With the variable-angle optical system that can enter the surgical field and the high resolution it provides, areas that are impossible to see with a surgical microscope can be displayed. The neuro endoscopy, which is successfully used in appropriate cases, helps to understand the relationship of the lesion with the surrounding tissues during surgery, to confirm that the entire lesion has been removed, and to provide bleeding control in the surgical field. For these reasons, the use of intraoperative neuro endoscopy in pituitary lesions surgery provides significant gains in terms of surgical treatment success rate.
Intraoperative Ultrasound (ioUSG): It is a dynamic imaging method that provides simultaneous high-resolution visual information during surgical procedures. With ioUSG, the location of the tumor and its relationship with surrounding tissues are determined exactly. The determination of the site of entry to the tumor during surgery is a guide for the surgeon on important issues such as determining whether the tumor has been completely removed. ioUSG can be used in both transcranial and transsphenoidal interventions. Intraoperative USG, which requires experience in use, provides superiority to other imaging systems due to its rapidity, simultaneous image delivery, and unaffected brain displacement. It is possible to obtain safer and more successful treatment results by using intraoperative USG in appropriate cases.
Neuronavigation: It is a set of computer-aided technologies that show the relationship with localization and surrounding tissues for the safe removal of brain and spinal cord tumors. Image-guided neuronavigation systems have been developed to aid in the more reliable resection of brain tumors. In appropriate cases, the location of the lesion is determined more clearly before the surgery by using neuronavigation tools, and the surgical strategy is determined accordingly.
Intraoperative MRI (ioMRI): It is a system that enables MRI imaging of the surgical site and its surroundings at any stage of surgery. In appropriate cases, it can be used to evaluate the integrity and dynamic changes in the tissues in and around the lesion. ioMRI requires the use of specially designed operating rooms and MRI-compatible surgical devices. With this MR imaging performed during surgery, the surgeon reaches the most accurate information about the lesion and distinguishes the abnormal brain tissue from normal brain tissue. The quality of the MR device used to make this distinction is important. Thanks to the 3-Tesla MR used in our clinic, tumor, and surrounding tissues are imaged in detail.
MRI imaging during surgery helps to confirm that the entire tumor has been successfully removed. For these reasons, ioMRI gains importance in the surgery of relatively small lesions, especially in areas that are difficult to visualize, such as the skull base, where pituitary lesions are located. Together with ioMRI, the total extraction rates of the lesions and the success of treatment are increased.
In Yeditepe University Pituitary Diseases Clinic, patients are evaluated by our expert team and directed to the most appropriate treatment options.
All patients referred for surgical treatment are closely monitored by the multidisciplinary team specialized in the field before, during, and after the surgery.
In Yeditepe University Pituitary Diseases Clinic, surgery is performed at international standards with an experienced team and up-to-date technological infrastructure in pituitary diseases requiring close follow-up before, during, and after surgery.
This content was prepared by Yeditepe University Hospitals Medical Editorial Board.
”
See Also
- What is Hypoglycemia?
- Causes and Treatment Methods of Cervical Herniated Disc
- Brain / Spinal Cord Spine and Nerve Surgery (Neurosurgery)
- Did You Know That Our Bodies are Managed by Hormones?
- Misconceptions About Hypertension
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Spinal Fractures
- Narrow Cervical Canal and Myelopathy
- What is Hypertension?
- Chronic Pelvic Pain
- What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome/PCOS?
- The Hidden Problem Seen in One out of Every 10 Women: HIRSUTISM
- Persistent Headache May Be a Sign of Tumor
- The Purpose of Pituitary Diseases is to Avoid Waste of Time with the Right Treatment
- Pelvic Floor Muscles Should Be Addressed with a Multidisciplinary Approach
- Protect Children From Sports That Will Knock Their Head
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Can Occur If the Bacteria in the Gut Are Not Functioning Well
- Doctor Support for the Ban on Heading by Children
- Head Trauma Can Cause Permanent Damage
- Diabetes Mellitus and its Treatment
- Treatment of Pituitary Adenomas
- Pituitary Clinic | FAQs
- What are Pituitary Diseases?
- What is the Pituitary Gland, What are its Functions?
- What is Hirsutism?
- Hirsutism Clinic / FAQs
- Treatment Success in Brain Tumors Also Depends on the Family
Alo Yeditepe