Alo Yeditepe
Alo Yeditepe
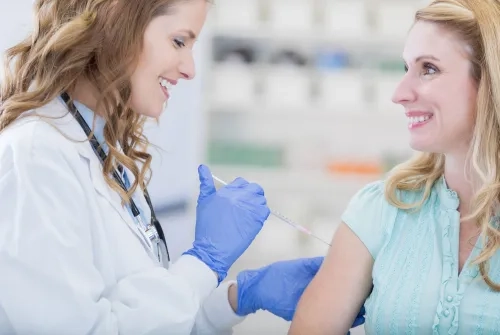
Which Vaccine Should Be Given to Adults and When?
Immunization with vaccines is considered one of the most effective methods to protect against certain infectious diseases with a certain and serious course. Yeditepe University Kozyatağı Hospital Infectious Diseases Specialist, who says that protection from infectious diseases has become much more important in today's conditions where antibiotic resistance is increasing, draws attention to the importance of vaccination in adults as well as children.
The importance of immunization in protecting against diseases that can threaten human life and cause serious consequences is increasing day by day. Yeditepe University Kozyatağı Hospital Infectious Diseases Specialist, therefore, underlines that immunization must start at birth and continue throughout life. At this point, the importance of vaccination, which is defined as active immunization, is revealed in adults as well as in children.
Long-term Protection Through Vaccination
Active immunization, which means that the body's immune system is activated during vaccination, says: "Vaccination with the vaccine requires a certain time (weeks or months) for the formation of antibodies/antitoxins. In other words, no protective effect (antibody/antitoxin) occurs immediately after the vaccination or after the first dose of the vaccine. In some cases, it may be necessary to administer more than one dose of the same vaccine at certain intervals for these to occur. Sometimes it may be necessary to repeat it at certain intervals in order to ensure the continuity of the effect of the vaccine applied against a certain disease. Some vaccines (live) create lifelong immunity after one or two doses of administration. Active immunization is often applied before exposure to microorganisms, that is, before transmission, in order to create antibodies/antitoxins against infectious diseases that are common in the society and have high infectiousness, with severe consequences."
Protective Effect Varies by Person
Reminding that no vaccine has a 100 percent protective effect today, our specialist said, "One of the factors that play a role in determining whether protective efficacy occurs after vaccination is the situation of the person who received the vaccine. The response of the body to the vaccine is weak in elderly people, overweight people, those with underlying chronic disease, diabetes, cancer patients, organ transplants, and those with all kinds of diseases that suppress the immune system or those receiving such drugs. Therefore, vaccination protection is lower in such people. On the other hand, it should not be forgotten that people who need to be protected against infectious diseases with vaccines come to the forefront of this group."
The Vaccine is Also Effective in Eliminating Certain Diseases
When immunization is carried out with the vaccine, not only is that person protected against the infectious disease but indirectly, the disease is prevented from being transmitted to other people. Therefore, the higher the number of people vaccinated against the disease in question in society, the lower the likelihood of developing that disease. It is also possible to completely eliminate some diseases. For example, thanks to successful vaccination programs, smallpox, measles, and polio have been completely eliminated or reduced to almost non-existent levels.
Anti-Vaccination Causes Re-Enhancement in the Prevalence of Some Infectious Diseases Around the World
Our specialist stated that some reports that "thiomersal", which has recently been included in vaccines to prevent bacterial and fungal growth and contains mercury, causes various harmful effects, especially autism, and that it increases vaccine opposition all over the world, and stated their views on the subject as follows:
"This led to a significant reduction in vaccination rates, and therefore the incidence of vaccine-preventable infectious diseases began to increase. Mercury (thiomersal), which is usually found in multiple vaccines, is ethyl mercury. This form does not accumulate in the body and is eliminated from the body within 30 days. On the other hand, mercury taken from various foods, especially shellfish, is methylmercury and accumulates in the body. The relationship between vaccination and autism is still a matter of debate today. Although no direct relationship was found between the administration of mercury-containing vaccines and autism, ethyl mercury was removed from the vaccines administered in the UK, America, and Europe, especially in the childhood age group. Considering these examples, it is thought that the administration of non-mercury vaccines, especially in the childhood age group, is important both in terms of reliability and in terms of eliminating the debates about autism."
Vaccination Should Not Be Forgotten Before Traveling Abroad
Although not routinely administered, typhoid vaccine, cholera vaccine, yellow fever vaccine, tick-borne encephalitis vaccine, and leptospirosis vaccines should be given according to the countries to be traveled to during travel.
At What Age Should Adults Be Vaccinated?
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis: The vaccine, which is started after birth, is regularly continued in childhood and adults, and re-vaccination is continued with doses every 10 years for life. It can also be used safely in people whose immune system is suppressed.
- Measles-Rubella-Mumps-Chickenpox: if these diseases have not been previously treated or vaccinated against them, one or two doses of vaccine are given in the adult age group. Since these vaccines are live virus vaccines, they cannot be administered during pregnancy and for those with suppressed immune systems.
- A shingles vaccine is given in two doses after the age of 50. Since it is a live virus vaccine, it is not given to pregnant or immunocompromised people.
- Pneumococcal vaccine: Everyone after the age of 65, or people with chronic disease or immunosuppressive disease, regardless of age, is given conjugate and polysaccharide pneumococcal vaccines at any age.
- Influenza vaccine: It should be administered annually at any age to anyone aged 65 years and above, or to persons with chronic disease or immunosuppressive disease.
- Hepatitis B vaccine: If it has not been previously protected by hepatitis b or vaccination against it, it is immunized with 3 doses of vaccine in the adult age group.
- Hepatitis A vaccine: If hepatitis A has not been previously passed or vaccinated against it, immunity is provided with 2 doses of the vaccine in the adult age group.
- Human papillomavirus vaccine (HPV): It is immunized with 3 doses of the vaccine from the age of 9 to 26 in women and 21 in men.
- Meningococcal vaccine: 2 doses of the vaccine are provided to people who have been removed from their spleen and have an advanced immune system, and to people who will travel to countries where the disease is intense.
- Haemophilus influenza B vaccine: It is immunized by administering 3 doses to people who have had their spleen removed or undergone a hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
This content was prepared by Yeditepe University Hospitals Medical Editorial Board.
”
İlgili Yazılar
- What Are the Benefits of Eating Fish? How to Choose Fresh Fish?
- What is Caffeine? Is Caffeine Beneficial or Harmful?
- Fall from Height Led to Kidney Failure, Saved by Sister's Donation
- What are Hip Joint Diseases? Causes and Treatment
- How Should We Eat for a Healthy Gut?
- How Should Diabetes Patients Eat?
- What is Venous Insufficiency? Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Methods
- How to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes?
- What is a Liver Transplant, How is it Done? and Who is it For?
- What is the Lipedema Diet?
- Journey of Hope from Georgia to Turkey: 63-Year-Old Father Donates Kidney to Son
- Does Secondhand Smoke Increase the Risk of Breast Cancer?
- How to Cleanse Your Lungs?
- What is Laryngeal Cancer? Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment Methods
- What Are Weight Loss Injections? How Are They Used?
- What is Laparoscopic Reflux Surgery and How is it Performed?
- What is Neurological Rehabilitation?
- What is Endometrial Cancer? Endometrial Cancer Symptoms and Treatment
- What is Whooping Cough? The Importance of Whooping Cough Vaccination During Pregnancy
- What is a Parathyroid Adenoma? Symptoms and Treatment
- What is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
- Anterograde Pyelography, Nephro Cystography, Anterograde Urethrography
- Stomach-Duodenum X-ray
- Birthday Gift Becomes a Gift of Life: Kidney Donation from Husband of 20 Years
- What is a Bypass? How is Bypass Surgery Performed?
- What is Constipation? What Helps With Constipation?
- Infections Common in Hot Weather
- What is Hepatitis B? What are its symptoms? How is it Transmitted?
- What is Heart Rhythm Disorder (Arrhythmia)? Symptoms and Causes
- Can Liver Cancer Be Prevented?
- What Are Head and Neck Cancers? Diagnosis and Treatment
- What is Vitamin A? What are the benefits of Vitamin A?
- What is Hypoglycemia?
- Contraceptive Methods: Birth Control and Effective Protection Options
- What is Parkinson's Disease? What are the Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease?
- What is Black Cumin? What are the Benefits of Black Cumin Oil?
- Causes and Treatment Methods of Cervical Herniated Disc
- Is Breathing Air Dangerous in Fires?
- Is Swallowing Cat Hair Dangerous?
- How to Cleanse the Liver the Fastest?
- What is Selenium? What Does It Do? What are the Benefits?
- What is Molluscum Contagiosum? What are the Symptoms?
- Surgical Treatment of Heart Valve Diseases
- Revision Surgery in Obesity Surgeons
- Common Misconceptions About Kidney Transplantation
- How Do We Know When We Have a Heart Attack?
- Breast Repair After Cancer
- What is Ovarian Reserve?
- What is Glutathione? What are the Benefits of Glutathione?
- Does the Sweltering Heat Affect Our Mental Health?
- Brain Health is Determined by Lifestyle, Not Age!
- Damages of Fake Sunglasses
- What is Genetic Testing? In Which Situations Is It Performed?
- What is Sudden Cardiac Death? What are the Symptoms?
- Uterine Polyps, Symptoms and Treatment
- What is Vitamin E?
- Genetic Diagnosis in IVF Treatment
- How Should Patients Receiving Chemotherapy Eat?
- What is Chemotherapy? How is it Applied?
- 19 Years Old Davut MİNAZ, Who Lost 45 Kilos in 4 Months, Clung to Life with His Father's Kidney
- Pregnant School
- Which Vaccine Should be Given in Adolescence and When?
- Robotic Hip Replacement Surgery
- What is Alpha Lipoic Acid? What are the Benefits of Alpha Lipoic Acid?
- Who Gets Colon Cancer?
- What is Coenzyme Q₁₀? What are the Benefits of Coenzyme Q₁₀?
- Kidney Diseases and Treatment Methods
- What Happens at 3rd Weeks of Pregnancy?
- What Happens at 2nd Week of Pregnancy?
- What is Colostrum? What are the Benefits of Colostrum Milk?
- What is Scoliosis? Exercise Methods in Scoliosis Treatment
- What is Curcumin?
- What is Vitamin B12? What are the Symptoms of B12 Deficiency?
- Ways to Treat Anxiety Disorder Without Medication
- What is Obesity? Obesity Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
- Knuckle Cracking Can Be Dangerous When It Becomes a Habit!
- What are the Problems Requiring Gallbladder Surgery?
- What is Endometriosis? What are the Symptoms of Endometriosis?
- Things to Consider When Walking in Snowy Weather
- Gallbladder Surgery is a Necessity, Not a Choice
- Pudendal Nerve Compression
- Curiosities About Cerebral Palsy
- What is an Antidepressant? What Does It Do? How Are Antidepressants Used?
- Precautions to Take Protecting Children from Infections
- What is HMPV Virus? HMPV Symptoms and Ways of Transmission
- What is Electronic Cigarette Disease (EVALI)? EVALI Symptoms and Treatment
- What is Hallux Rigidus (Stiff Big Toe/Toe Arthritis)? Symptoms and Treatment
- What is Hallux Valgus (Bunion)? How is it Treated?
- Why Is the Flu Lasting Longer This Year?
- Stomach Cancer Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- Tips to Restore Balance to Your Body After New Year's Eve!
- What is Mythomania (Pathological Lying Disorder)? What Causes Mythomania?
- What is Shingles? Shingles Symptoms and Treatment
- What is Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)? How is HRT Performed?
- What is Ferritin? Low Ferritin and High Ferritin
- What is Cataract? Symptoms and Treatment
- What is Hemoglobin (HGB)? Low and High HGB
- What is Colon (Intestinal) Cancer? Symptoms and Treatment
- What is a Bone Tumor? Bone Tumor Symptoms
- What is Calcitonin Hormone? Calcitonin Hormone Deficiency
- What is Emotional Hunger? How Does It Arise?
- Does Breast Milk Protect Against Diseases?
- Benefits of Spices
- What is COPD? Symptoms and Treatment of COPD
- What Causes Nausea? What is Good for Nausea?
- What is Organ Donation?
- What are the symptoms of a Panic Attack? How to Overcome a Panic Attack?
- What is Heartburn? What is Good for Heartburn?
- What is Coronavirus?
- Intravenous Pyelography (IVP)
- Enteraclysis (Small Intestine)
- What is Mommy Makeover?
- Meniscus and Cartilage Transplantation Can Be Done at the Same Time
- Benefits of Being Limber
- What is DMD Disease? Symptoms and Treatment
- What Does Narcissist Mean? Narcissistic Personality Disorder
- The Relationship Between Gut Microbiota and Obesity
- At What Age Should Children Start Using Social Media?
- Hormonal Disorder Symptoms and Treatment
- Causes and Treatment of External Ear Inflammation
- What is Heel Blood? Why is heel blood taken?
- What is West Nile Virus? What are the Symptoms and how is it Transmitted?
- What is Crooked Leg? Can Crooked Legs Be Treated?
- What is Predisposition to Allergy (Atopy)?
- What is Fatty Liver?
- What is Good for Diarrhea? How to Treat Diarrhea?
- What is Vaginal Infection? What are the Symptoms?
- The Importance of Sexuality in Marriage
- What is HPV? What are the Symptoms of HPV? How is it Transmitted?
- Viral Hepatitis and Prevention Methods
- What is Ureaplasma? How is Ureaplasma Treatment Done?
- Benefits of Water
- Long Journeys Increase the Risk of Embolism!
- He Went to the Hospital with Leg Pain, Discovered His Carotid Artery Was 95% Blocked
- The Use of Botox in Neurological Diseases
- Hand Foot and Mouth Disease Symptoms and Prevention Methods
- What Asthma and COPD Patients Should Pay Attention to When Using Air Conditioning!
- Does Sunburn Cause Skin Cancer?
- Risk Factors in Heart Diseases
- What is the Ideal Age for Marriage?
- COVID-19 New Variant
- ThuFLEP Treatment Improves Quality of Life in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Does an Aortic Aneurysm Show Symptoms ?
- How Often Should You Take a Shower?
- What is Parvovirus B19 (Fifth Disease)? What are the Symptoms of Fifth Disease?
- Radioembolization in Liver Tumor Treatment
- What is a Neck Mass?
- Treatment of Urinary System Stones with Thulium Fiber Laser
- What is Allergy? What are the Symptoms of Allergy?
- ThuFLEP Method in Benign Prostate Enlargement
- What is Pelvic Floor? What are Their Duties?
- What is Desert Dust? Harms of Desert Dust
- What is Measles? Symptoms and Treatment
- Heart Valve Diseases and Treatment Methods
- Is Cancer a Treatable Disease?
- What is Gallbladder Surgery?
- Healthy Nutrition Suggestions during Ramadan
- What is Tuberculosis (TB)? Symptoms and Treatment
- How Do Heart Disease Risk Factors Affect Women and Men?
- Colorectal Cancers and Treatment Methods
- What Causes Shoulder Dislocation? Shoulder Dislocation Treatment
- What is a Heart Attack? What are the Symptoms of a Heart Attack?
- Skin Rejuvenation With BBL Laser
- What is Parkinson's Surgery?
- The Most Common Diseases in Women
- What is Hysteroscopy? Hysteroscopy Usage Areas
- What is Myoma? Myoma Symptoms and Treatment
- Knee Pain
- What is Prostate Cancer? Symptoms and Treatment
- What is Broken Heart Syndrome? Symptoms and Treatment
- What Causes Skin Blemishes? How to Get Rid of Skin Blemishes?
- Lymph Node Swelling
- What is Risky Pregnancy?
- Frequently Asked Questions About HPV Vaccine
- Childhood Cancers and Treatment
- 9 Tips to Enter the New Year Without Gaining Weight
- Nose Aesthetic Surgery - What You Need to Know
- What Precautions Should Be Taken Against the Cold Epidemic?
- Wrist Pain Causes and Treatment
- BBL Laser: What is Broadband Light Therapy?
- Don't Be Late Fighting Against Diseases
- Brain / Spinal Cord Spine and Nerve Surgery (Neurosurgery)
- Current Approach to Dizziness Treatment: Balance Perception Rehabilitation
- How Should Those with Kidney Stones Eat?
- Patched Solution for Umbilical Hernia
- What are the Symptoms and Treatment Methods of Cirrhosis?
- Early Menopause and Ovarian Failure Can Be Prevented
- Benefits of Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation in Spinal Cord Injury
- Special Nutrition Recommendations for the Eid
- How Can We Protect Children from COVID-19 Coronavirus?
- Control Your Weight During the Holiday with Small Adjustments in Your Habits
- Lumbar Spondylolisthesis (Lumbar Slipped Vertebrae)
- Do not Risk Going Blind While Trying to Have Colored Eyes
- Tonsillectomy in Children
- 10 Questions About Kidney Transplantation
- Ergonomics in Automobiles Prevents Accidents
- The True Face of the Protein Myth
- What is Fractional Carbondioxyde Laser?
- Antibiotics Kill Beneficial Bacteria, Not Viruses
- Allergies in Children Can Increase During the Summer Months
- Nutrition in Cancer
- Cancer Treatment Methods
- Don't Underestimate Bone Pain That Doesn't Make You Sleep and Doesn't Relieve With Medication
- Ways to Prevent Sepsis
- The Most Preferred Aesthetic Surgeries
- What is Anxiety? What are the Symptoms of Anxiety?
- What is Lodine Deficiency? What are the symptoms of Iodine Deficiency?
- Carotid Artery Disease
- What is Renal Denervation?
- BBL Rosacea Treatment
- What is Intravenous Ultrasound (IVUS)?
- What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, How is it Treated?
- What is Golden Needle?, How is Golden Needle Treatment Done?
- Circadian Rhythm Disorder
- Palpitations in Children
- Genetic Tests in Cancer
- Renal Denervation in Hypertension Treatment
- Is Lymphoma (Lymph Cancer) a Treatable Disease?
- What is Peer Bullying?
- Joint Pain and Causes of Joint Pain
- Lung Cancer Screening Age
- What is Rhinoplasty? Who Can Undergo It?
- What is TAVI?
- What is Good for Cough? How to Cure Cough?
- Flu Vaccination in Children
- Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Methods
- What is Antibiotic Resistance?
- Lung Cancer Symptoms and Treatment
- What is Laparoscopic Surgery in Gynecology?
- Walking and Returning to Social Life After Knee Replacement Surgery
- What is Fibromyalgia Syndrome?
- Fibromyalgia in Children
- How Should the Daily Salt Consumption Amount Be?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Breast Reduction Surgery
- What is a Stroke (Apoplexy)?
- Menopause Symptoms and Menopause Treatment
- What Are the Benefits of Beets?
- Hormone Disruptors
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and its Treatment
- What Are the Advantages of Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery?
- What is an Aortic Aneurysm? How is it treated?
- Suggestions to Get Rid of the Menopause Belly
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Get Your Child's Eye Examination Done Before They Go to School!
- Robotic Knee Prosthesis Surgery
- Swallowable Gastric Balloon
- Spinal Cord Injuries and Symptoms
- What Is Rose Disease? Symptoms and Treatment of Rose Disease
- Things to Know About Sepsis
- Why Does Ankle Pain Occur? What Is the Treatment?
- Why Are We Hungry at Night?
- 10 Ways to Have a Sound Sleep in the Heat
- What Are the Symptoms of Gallbladder Stones? How Is It Treated?
- Foods to Help Quench Your Thirst on Summer Days
- Benefits of Breast Milk and Breastfeeding
- What is the Eris Variant? What are the symptoms of the Eris Variant?
- Dealing Ways with Overtemps
- "Is the Watermelon Diet Healthy?
- What Is Reflux?
- How to Protect Brain Health?
- Congenital CMV Infection in the Neonatal Period
- Epilepsy Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Methods
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Disease, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Electromagnetic Stimulation in the Treatment of Endometriosis and Infertility
- The Treatment of Breast Cancer and the Repair Process of the Breast are a Whole
- Hot and Humid Air Affects Our Breathing Quality
- What Causes Hip Pain? How Does Hip Pain Go Away?
- What is Hepatitis? What are the Symptoms and Treatment Methods?
- Services Available at In Vitro Fertilization Center
- The Usage Area of Robotic Surgery Expands in Orthopedic Surgeries
- After a heart attack, the risk of mortality is higher in women than in men
- What is Myasthenia Gravis Symptoms and Treatment Methods
- When do Babies Start Walking?
- When do Babies Start Talking?
- Symptoms and Treatment Methods of Cirrhosis
- What is Cirrhosis? What Causes Cirrhosis
- If the Size of the Thyroid Nodule is Over 4 cm, Be Cautious!
- Ways to Boost Mental Resilience
- Symptoms and Treatment of Tick Bites
- Sunburns Can Leave Permanent Damage
- Can Uncontrolled Use of Medication During Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Disabilities in Children?
- Is Hypertension Seen in Young People?
- What is Hypertension? Symptoms and Treatment Methods
- Maigne Syndrome and Treatment
- He Couldn't Breathe; He Regained His Health with the Application of 3 Different Special Surgical Techniques Together
- The Father-Child Relationship Reflects on Personality Traits
- Higher Risk of Anterior Cruciate Ligament and Ankle Injury in Female Athletes
- Persistent Fatigue of Unknown Cause Could Indicate MS!
- 12 Suggestions to Make Life Easier with Fibromyalgia
- Summer Infections
- 8 Causes of Sweating
- Superfoods
- What Should Asthma Patients Be Cautious About?
- Does Poor Quality Sleep Increase The Risk of Asthma?
- Precautions Must Be Taken Against Loss of Life Due To Infection in Thalassemia
- Early Diagnosis Saves Lives in Insidiously Progressing Kidney Tumors
- Puberty
- Causes of Hair Loss
- Non-Surgical Treatment of Reflux
- How Does Working Life Affect Prospective Mothers?
- Factors Affecting Growth in Children
- Thyroid Gland Diseases in Children
- Diabetes in Children
- Special Care for Premature Babies
- Frequently Asked Questions about Detox
- Liver Transplant Process and Hospitalization
- Itching can be a Symptom of Another Disease
- Dehydration can Lead to Forgetfulness in the Elderly
- What Causes Sleep Problems in Babies?
- Neurological Involvement
- Families with Children Who Have Autism Should First Accept the Situation
- Did You Know That Our Bodies are Managed by Hormones?
- Sweating May Be a Sign of Illness
- Information on H1N1 (Swine Flu)
- Summer is Coming... Beware of food poisoning!
- Can Women With Gynecological Cancer Have Children?
- Voice Can be Lost If Tracheal Stenosis is Not Detected Early
- Negative Effects on Early Menopause Health
- Causes of Female Infertility
- How Does High Calcium in Blood Cause Complaints?
- Experts Warn Students Before the Exam!
- Boost Your Immunity Naturally
- What is HCT (Hematocrit)?
- Beware of Joint and Muscle Pain in the Winter Months!
- What is Allergy? What are Allergy Symptoms?
- The Physician's Garden of Dreams
- What are the Nutrients That Stress Digestion?
- Key Parts of Children's Nutrition on Holidays
- Can Cervical Cancer in Women Be Prevented?
- Tips for Choosing a Babysitter
- Patients Who Undergo Joint Replacement Surgery Can Stand Up and Walk the Next Day
- Ear Pain During Flight Can Be a Sign of Some Diseases!
- The Use of Non-Inpatient Closed Surgery is Increasing in Gynecological Diseases
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
- Office Hygiene: The Most Common Areas Where Microbes are Found in the Office
- What Causes Insomnia, Diagnosis and Treatment
- Misconceptions About Hypertension
- Chronic Kidney Disease and Treatment Methods
- Lumbar Disc Herniation (Herniated Disc)
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Spinal Fractures
- Narrow Cervical Canal and Myelopathy
- Big Toes Can Be A Big Problem!
- All You Need to Know About Cervical Cancer
- The Rate Of Kidney Stones Has Begun To Increase In Women
- What is Hypertension?
- Unable to Speak Due to Her Illness, Sibel: I Could Not Tell My Children 'I am Here' During the Earthquake
- The Way to Prevent the HIV Pandemic Can Be Made with Awareness
- Our Taboos Affect the Increase in the Number of HIV-Positive Cases in Turkey
- A First in the Literature: Parathyroid Cell Obtained from Thyroid Stem Cell
- Scabies Disease
- Ways to Maintain Heart Health in Cold Weather
- 8 Important Benefits of Dry Legumes
- 9 Common Misconceptions About COPD
- Which Foods Should be Consumed Together?
- How to Approach a Child in Adolescence?
- Is Your Heart Ready For Winter?
- Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Asthma
- 3 Major Developments Shaping Treatment in Colon Cancer
- HoLEP Eliminates 85 percent of Drug Use in the Treatment of Benign Prostate Enlargement
- How Can We Manage Stress?
- Nutrition Recommendations for Diabetes Patients
- Can Weight Loss Despite Not Dieting Be a Sign of Cancer?
- Latent Diabetes (Prediabetes)
- A Child's Difficulty in Singing May Indicate a Voice Disorder!
- They Said He Could Never Speak Again Due to Laryngeal Cancer, But Today After the Surgery He Underwent, He Can Speak!
- "Vertigo Is a Treatable Condition"
- Long Lasting Sore Throat May Suggest Throat (Larynx) Cancer
- Causes of Hearing Loss
- Ringing in the Ears Does Not Mean Somebody Is Calling for You
- Treatments that Reduce Life Loss in Cancer Give Hope!
- What is Synovitis in Joints?
- Nasal Congestion in Children May Prevent the Development
- Vitamin Deficiency May Cause Dizziness
- Hip Osteoarthritis and Hip Prosthesis
- Balloon Sinuplasty
- Pool and Hot Weather Trigger Ear Eczema
- Hip Impingement Syndrome
- Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
- Hearing Health
- Fight Chronic Sinusitis
- Allergic Rhinitis Targets People in Big Cities
- Can Nutritional Defects Underlie Middle Ear Inflammation?
- Do not Let Your Fear of Tampons Delay Your Nose Surgery
- Strep A Symptoms and Treatment
- What Diseases Can Insomnia Cause in Children?
- Stem Cell May Be the Future Cure to Hearing Loss with Bionic Ear as Hope
- Warning from the specialist: "Beware if your child turns up the volume of the TV too loud!"
- Nasal Sprays Can Be Addictive!
- What is the Future of Treating Cartilage Problems?
- Not Only Athletes Suffer from Meniscus Tears!
- Is Cartilage Damage More Common in Those Who Run for Long Periods?
- Sudden Hearing Loss and Dizziness Can Lead to Irreversible Results If Not Treated!
- Beware If Your Shoulder Or Neck Pain Lasts Longer Than Two Days After Swimming!
- Mistakes While Swimming Can Cause Shoulder Pain
- What is a Stress Fracture? How to Treat Stress Fracture?
- Wear Heeled Shoes Against Heel Spurs
- Improper Use of Phones, Tablets and Computers Increases Elbow Pain
- Does Your Shoulder Strain When Lifting Your Arm?
- Myths About Fractures
- Adenoid and Tonsil Problems in Children
- Endocrine Disease May Also Be the Cause of Bone, Joint, and Muscle Pain
- Be Careful in the First 24 Hours of Hip Fractures!
- Vitamin D Deficiency May Be The Cause Of Your Joint Pain
- The First Onset of Pain in Cartilage Damage in the Knee Should Not Be Overlooked
- Have Your Baby Take Their First Steps in Good Health
- Heavy School Bags Can Cause Pain in the Lower Back, Shoulders, and Hands!
- What is Epilepsy?
- Chronic Pelvic Pain
- Diagnosis in Thyroid Diseases
- Assessment of Hyperthyroidism
- Hashimoto's Thyroid Disease
- Thyroid Tumor (Cancer)
- Graves' Disease
- Thyroid Nodules
- Thyroid Surgery
- Assessment of Hypothyroidism
- What is the Harm of High Calcium in the Blood?
- Frequently Asked Questions in Thyroid Diseases
- What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome/PCOS?
- Mushroom Poisoning
- Postpartum Exercise Stages for People Who Had Vaginal Delivery
- Postpartum Exercise Stages for Those Who Give Birth by Cesarean Section
- What is the Goal in Newborn Intensive Care Treatment?
- Postpartum Period
- 7 Effective Tips Against Urinary Incontinence
- Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate
- Diagnosis of Heart and Brain Diseases with PET CT
- Atomic Therapy (Radioactive Iodine Therapy)
- Therapies Applied in Nuclear Medicine
- Theragnostic Approach in Cancer Treatment
- Nuclear Medicine Diagnosis and Imaging
- How to Choose Baby Clothes?
- What Are Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions?
- Multiple Myeloma
- What are Capsule Treatment Methods in Stomach, Small, and Large Intestine Screening?
- Adult Bone Marrow Transplantation / Inpatient Guide
- Do Not Put a Cigarette Butt or Pour Olive Oil or Liquid Soap on the Tick
- Sports Injuries
- Importance of Physical Exercise for Cardiovascular Patients
- Gastroenterology Procedures
- The Sole Remedy for Chronic Renal Failure is Transplantation!
- Watch Out Blue Light Emitted By Devices For The Health of Your Eyes
- Cartilage Transplantation from Donor Has Been Started to Perform in Turkey
- Paternal Prostate Cancer is a Risk Factor for Breast Cancer in Daughter
- Has Your Child Adapted to School?
- Things Wondered About Kidney Transplantation and Organ Donation
- Health Coming with Spring: Purslane
- An Infection that Does Not Recover is a Precursor of Diabetes
- Sperm Will Be Produced from Stem Cells Soon
- You Can Be Protected from Varicose Veins During Pregnancy
- Reflux Complaints Have Increased in Babies!
- Is the Incidence of Reflux Increasing Among Children?
- The Game of Chromosomes
- Let the Bonding Between Mother And Child Not Be Sacrificed for Success!
- If You Consume More Than 5 grams of Salt...
- Nose Surgery without Tampon is Possible
- Do Not Underestimate Itching!
- Intense Stress Makes Hair Ringworm
- Urticaria Decreases the Quality of Life
- Reheat the Food You Cooked Only Once!
- HIV Can Be Hidden for 10 Years without Any Symptoms!
- 290 Million People Live Without Knowing They Have Hepatitis
- Which is the Ideal Birth for You?
- The Frequency of Hepatitis Seen in Dialysis Patients Is Decreasing
- Pay Attention When Consuming These Nutrients!
- Things to Consider When Touching Meat at Eid
- What Is Anthrax Disease?
- Set the Rules from the Beginning!
- How Do You Approach a Child Who Is Reluctant to Go to School?
- What to Consider When Feeding Our Children in Hot Weather?
- Childhood Lymphoma Treatments Give Hope!
- 10 Important Myths in Alzheimer's Disease
- Even If You Gain Weight When You Quit Smoking, Your Risk of Heart Disease Decreases
- What is Menopause? When Does Menopause Age Begin? What are the Symptoms of Menopause?
- 4 Tips to Boost Your Immunity in Seasonal Transitions
- The Biggest Obstacle to Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer: LACK OF INFORMATION
- Pain Control Boosts Cancer Treatment Success by 80 Percent
- Is Breast Cancer a Chronic Disease?
- The Biggest Question for Working Mothers: Who Will Take Care of My Child?
- High Chance of Treatment in Childhood Leukemia
- 12-Year-Old Tuğba Nur Survived with Transplant
- One in 7 Pregnant Women Has Diabetes
- COPD Makes You Age Early
- Sudden Change in Baby May be Growth Spurt
- The Way to Fight AIDS is to Raise Awareness First
- What is a Premature Baby and How to Feed it?
- Be Careful When Consuming Sage During Pregnancy
- Time to Learn Responsibilities
- 6 Ways to Protect Your Skin in Winter
- The Concern of Being a ‘’Good Mother’’ in Pregnancy
- It is Possible to Lose Weight by Dominating Your Brain
- Early Diagnosis is very Important to Prevent Glaucoma from Resulting in Blindness!
- Turkish Neurologist Discovered a New Diagnostic Method
- Nasal Sprays Can Be Addictive
- Still Not Too Late For Flu Vaccine
- If Your Child is Constantly Getting Sick in the Winter, It Could be Due to Allergies
- Ways to Deal with Work Stress
- Even If Your Child is Sick, They Must Take a Bath
- What is Rhinovirus?
- What Diseases Does Stem Cell Transplantation Cure?
- Beware of Multiple Myeloma!
- It is Possible to Protect Children From Diseases with Simple Precautions
- The Hidden Problem Seen in One out of Every 10 Women: HIRSUTISM
- Had Kidney Transplantation, Recovered from Heart Failure!
- Ways to Undergo Flu Easily
- HPV Infection Also Affects Men, Not Just Women
- Promising Developments in Childhood Cancers
- Even Parents Should Not Kiss Their Baby
- When Should Adenoid Surgery Be Performed in Children? When Should It Not Be Done?
- Knee and Hip Arthroplasty Boosts Quality of Life
- The Usage Area of Closed Surgeries in Gynecology is Expanding
- The Chance of Becoming a Father Increases with Microchip Technology
- 30-Year Imam Regains His Voice With Voice Therapy
- Treated For Asthma For Two Years But Has Had A Tumour In Her Trachea
- What Should Be Considered In Preventing Home Accidents For The Elderly?
- Treatment without Tampons in Nasal Surgeries
- Vaccine Rejection Can Lead to Irreversible Problems!
- Allergy and Asthma During Pregnancy
- Persistent Headache May Be a Sign of Tumor
- Eye Trauma in Children Can Cause Glaucoma
- Excess Protein Does Not Increase Muscle Mass, and It Impairs the Kidneys
- Myths About Salt
- Mediterranean Diet Prevents Developing Colon Cancer!
- It Is Aimed to Eliminate Tuberculosis Worldwide By 2030
- Consanguineous Marriage Increases the Risk of Epilepsy 40 Times
- Environmental Factors and Obesity Increase Risk of Multiple Myeloma
- Serious Risk Factor for Colon Cancer: Heredity
- The Purpose of Pituitary Diseases is to Avoid Waste of Time with the Right Treatment
- Importance of Vaccination in Children
- Chance of Treatment in Patients Who Have a Tube Inserted in Their Throat to Breathe
- 9 Points to Be Considered for a Healthy Ramadan Month!
- Fighting with Thalassemia: Meral Yılmaz
- Thalassemia Spreads from the Mediterranean to the Whole of Europe with Migration!
- Thanks to the Ovarian Rejuvenation Method, She Counts the Days for Birth!
- Pollen is Now Seen Outside of Seasonal Changes
- Thalassemia Trait Rate in Turkey is High
- Consult a Physician Immediately If Your Child isn't Growing Tall Enough
- Emotional Eating May Be the Cause of Your Weight Gain
- Beat Breast Cancer at a Young Age With Faith and Ambition!
- How Should We Protect Our Skin During the Summer Season?
- 2% of School-Age Children Have This Problem
- Choose Proven Treatments, Not Alternative Methods in Cancer Treatment!
- Beware Information Pollution About Cancer!
- Pelvic Floor Muscles Should Be Addressed with a Multidisciplinary Approach
- 8 Tips for Fathers Who Want to Develop Healthy Relationships with Their Children
- 10 Tips to Help You Get Rid of Your Holiday Weight
- Protect Children From Sports That Will Knock Their Head
- Early Treatment of Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic Fever is Vital
- Imaging Center / Education and Research
- Patient Preparation Information
- Dacryocystography (Tear Sac and Tracts)
- Pediatric CT
- Pediatric MRI
- Neuro Radiology
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Multi Slice CT
- Soft Tissue Ultrasonography
- Extremity CT
- Ultrasound and Doppler Ultrasonography
- Fluoroscopy
- Digital X-ray
- Cystography, Retrograde Cystography, Fractionated Cystography (Progressive Cystography)
- Voiding Cystography, Voiding Cystourethrography, (Micturition Cystourethrography)
- TRANSVAGINAL US and Doppler Us
- Cyanography (Salivary Glands)
- Portal and Main Vascular Doppler Us
- Colostomy, Ileostomy Radiography
- Colon X-ray (Single or Dual Contrast)
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
- T-Tube Cholangiography (Biliary Tract)
- Lower Abdomen CT
- Radiology of Abdomen
- Oral Cholecystography (Gallbladder and Pathways)
- Renal Doppler Us
- Virtual Colonoscopy CT
- TR Doppler Us - TRUS
- Whole Abdomen CT
- Upper Abdomen CT
- AV FISTULA Should Be Done At The Right Time For Hemodialysis Patients
- Tests That Need to Be Performed During Pregnancy
- The Healthiest Summer Fruits
- Kidney Reflux Should Be Suspected in Children with Urinary Tract Infection
- Toy Guide for Your Baby
- Pay Attention to Kidneys in Pregnancy!
- Shining Star of the Tables: Probiotics
- First Check-Ups for Your Baby After Birth
- Breakthrough Innovations in Colon Cancer
- He Held On To Life with His Brother's Kidney
- 'Exercise Vaccine' Recommendation for Chronic Fatigue
- 70 of the 7 Thousand Chemicals in That Smoke Cause Cancer
- The Most Common Skin Rashes in Newborns
- Do Ovarian Cysts Prevent Childbearing?
- School Stress Invites Sleepwalking
- Taking a Leave Is as Useful as Quitting Smoking
- Father Who Lost His Daughter to Leukemia Saved a Life Through Stem Cell Donation
- He Came to Turkey to Get Rid of the Colostomy Bag
- Preschool Health Checks Increase Socialization and Success
- Daughter-in-Laws Care for Alzheimer's Patients
- Mother-in-Law Gives Her Kidney to Her Son-in-Law of 23 Years
- Mistook It for Flu and Found Out She Had Stage 4 Lymphoma
- Ten Hints for Providing Care for Premature Babies
- The Expected Moment Has Arrived; Birth Begins
- Are Pre-School Health Checks Done?
- Long-Term Low Carbohydrate Consumption Triggers Heart Disease
- The Problem may be the Lack of Self-Confidence!
- Breast Protective Surgery Is Not Recommended in the Treatment of Multifocal Breast Cancer
- Breastfeeding Increases the Baby's Self-Confidence
- Why is Headache Important During Pregnancy?
- 9 Most Common Types of Cancer in Children
- Diarrhea and Constipation Increased in Those with Irritable Stomach
- He Beat Leukemia, Made A Graduation Ceremony in His Hospital Room, and Won the University
- Which Tests Should Expectant Mothers Not Neglect? What Tests Should Be Done While Pregnant?
- Some Patients Go Through Menopause Even at the Age of 15
- Does Breast Cancer Risk Decrease During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding?
- For Every 10 Kilogram Gain, the Risk of Sleep Apnea Doubles!
- Children Whose Parents Are Allergic Are More At Risk
- Which Imaging Method Should Be Used for Breast and When?
- I Was Waking Up With Stomach Pain, I Fell Better After Endoscopic Fundoplication
- Breast Cancer Incidence Age Is Decreasing Day by Day
- Stress Disrupts the Menstrual Cycle
- Anemia, Constipation, and Vomiting of Unknown Cause Can Be Dangerous
- What Precautions Should Be Taken for Neuromuscular Diseases?
- Eating Calories In The Morning Saves Lives
- Do Dental Caries Increase the Risk of Pneumonia?
- Importance of Pneumonia and Flu Vaccine
- Myomas Can Grow During Pregnancy
- The Hidden Danger That Threatens the Immune System: Food and Drugs
- The Risk of High Blood Pressure Increases as You Go to High Altitudes
- As the Western Diet Increases, So Does Stomach Cancer
- Recommendations From The Expert For Migraine Patients
- Decrease in Muscle Mass Starts at Early Age
- The Warrior That Protects Our Immune System: Vitamin D
- This Disease Can Manifest Itself When Children Walk Late
- Lung Patients Should Not Stop Their Medications
- As Insomnia Increases, Its Harmful Effects on the Immune System Also Increase
- Young Man Who Lost His Voice Due to Tracheostomy Regained His Voice After Months
- Useful Bacteria Increases IVF Success
- 8 Tips for Better Sleep
- The Immune System and Sleep Are Sending Messages to Each Other for A Healthy Life
- Maintaining Immunity During Ramadan
- Celiac Disease May Be the Cause of Growth Retardation in Children
- Do not Hide From Your Doctor That You Are Fasting
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Stroke
- Eye, Kidney, and Heart Enemy: Hypertension
- Is Hot Chemotherapy the New Hope for Advanced Stage Cancer Patients?
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Can Occur If the Bacteria in the Gut Are Not Functioning Well
- Ramadan Warning for Those Who Experience Stomach Disorders
- 13 Ways to Relieve a Headache Without Medication
- By 2025, Hypertension Patients Are Expected to Reach 1.5 Billion
- Iron Deficiency is Vital
- Every Three Minutes, A Child Is Diagnosed With Cancer In The World
- Vitamin D Deficiency Disrupts the Course of MS
- Approximately 3 Million Patients Need Blood Transfusions Every Year in Turkey
- Recommendations to Strengthen the Immune System
- Cervical Hernia Can Be Confused with Cervical Kyphosis
- No Obstacle to Having Screening Tests in Gynecological Cancers
- Kidney Failure Caused by Ear Obstruction
- Smoking Rates Under the Age of 15 Are Increasing
- Does Laziness Trigger Alzheimer's?
- Keep It Away From Packaged Products To Strengthen Children's Immunity
- Ways to Deal with Quarantine Weight
- 8 Mistakes That Can Affect Your Immune System in Quarantine
- Burnout Syndrome at Work Gains Weight
- Inhaling Electronic Cigarettes for a Few Minutes Causes Damage to Vein Wall
- Which Thyroid Nodule Can Be Treated Without Surgery?
- Poop and Urine Incontinence in Children Can be a Sign of Serious Disorders
- There is Still a Lot of Misconception About Organ Donation
- Healthy Recipes to Decorate Your New Year's Eve Table
- When to Get the Flu Vaccine
- Diabetes Aims the Feet
- Should You Become a Mother Before 35?
- She Was Relieved of Her Pain When the Missing Parathyroid Gland Was Found in The Chest Cavity
- Covid-19 Variants
- Blue Light May Cause Memory Weakness in Children
- Antibiotics Account For 14% of Prescription Costs
- 1 in 4 Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Have Depression
- 4 Significant Preliminary Symptoms of Lung Cancer
- Anesthesia-Related Loss of Life Declines to 1 in 100,000
- People Who Smoke More Than 25 Cigarettes a Day Have a 50-fold Increased Risk of Lung Cancer
- Good Results have been Achieved in Leukemia Treatment
- Gum Problems are Three Times More Common in Diabetic Patients
- One-third of Obesity In Adults Begins in Childhood
- Initial Symptoms of ALS Considered To Be Nerve Compression
- Children Should Be Away From Fast Food Toy
- Vitamin D May Be the Cause of Your Fatigue
- How Does Acid Rain Affect Human Health?
- Benefits of Antioxidant
- He Lost 20 Kilograms in 40 Days for His Wife
- 15 Ways to Protect Skin During Winter
- Do Individualized Treatments Offer Hope for Cancer?
- What Are the Birth Signs?
- Children's Eating While Studying Prepares the Ground for Obesity
- Can Infection Cause Permanent Hearing Loss?
- Soil Eating in Patients with Pica Syndrome
- Doctor Support for the Ban on Heading by Children
- Does Hypertension Lead to Growth Retardation in Children?
- Can Back Pain Be A Sign of Lung Cancer?
- One Out of Every Seven People Has Kidney Disease
- Imaging Methods During Pregnancy
- Permeable Bowel Syndrome Can Prepare the Ground for Diseases
- Cancer Predisposition Can Be Determined With This Test
- West Nile Virus Replaces Malaria
- Early Detection Is Cancer's Most Powerful Enemy
- The Cause of Shortness of Breath May be Trachea Stenosis
- It Is Necessary to Try to Be Healthy in order to Be Protected
- Ingrown Hair Is Not Just an Adult Problem
- Start the New Year Healthy
- Causes and Treatment of Abdominal Bloating
- Nine Out of Ten COPD Patients Do Not Know They Are Sick
- It Is Possible to Prevent Possible Complications of Intubation
- Drug Treatment is Priority Leg Vein Obstructions
- How Should Kidney Patients Be Protected From COVID-19 Coronavirus?
- Men Should Also Be Vaccinated Against Cervical Cancer
- After 16 Years, She Wanted to Be a Mother Again; She Experienced the Shock of Her Life
- Consanguineous Marriages Prepare the Ground for Muscle Diseases
- Air Pollution Threatens the Heart As Much As Smoking
- What Do Suspicious Mammography Results Mean?
- Genetic Testing Directs Our Health
- What is Propolis? How to Use Propolis?
- The Slowing Traffic in Istanbul Increases the Risk of Cancer!
- Phytotherapy May Reduce Side Effects of Cancer Treatment
- She Was Afraid of Endoscopy; She Found Out She Had Stomach Cancer 2 Years Later
- Immune System and Ways to Strengthen it
- Does an Egg Raise Cholesterol?
- Could the Cause of Insomnia be What We Eat?
- The Vicious Cycle of Generations with SMA Can Be Overcome with Screening Tests
- Working From Home Increases Waist and Neck Problems
- 6 Ways to Spend New Year's Eve Without Gaining Weight
- Multivitamin is Not a Panacea
- Omega-3 Deficiency Can Lead to Disease
- A New Flu Outbreak is Expected Every 10 Years
- Pay Attention to the Children Who Get Sick Often
- The Tumor in the Trachea was Removed Without Damaging the Vocal Cords
- 63% of Vector-Borne Diseases are Caused by Lyme Disease
- These Diseases Affect Women Differently Than Men
- Will the Hernia Heal on Its Own?
- Thyroid Storm Can Turn Life Upside Down
- Experts Warn About Flu Risk
- Suggestions to Prevent Children from Gaining Weight While Still
- Is Intermittent Fasting Beneficial?
- Misconceptions about the Female Heart
- Genetic Factors Can Increase Glaucoma Risk 7 Times
- Urinary Incontinence Causes Depression in Women
- Genetic Diseases Can Be Detected by a Blood Test in the Womb
- Hepatitis Disease Poses Risk for Esophageal Varices
- Age of Screening for Colon Cancer Decreased from 50 to 45
- Rashes That Require Attention in Children
- Breast Cancer Has Dethroned Lung Cancer for The First Time! But, Why?
- 7 Things to Consider When Choosing Sunglasses!
- Thyroid Diseases Require Careful Eye Examination
- Had Hepatitis B at 18, 20 Years Later She Clung to Life with Her Husband's Liver
- He Was Ashamed to Speak, and He Was Reborn with His New Voice
- Improper Nutrition Invites Kidney Failure
- Survived from Tumor Covering Half of Larynx With Closed Surgery
- He Walked Out Of The Hospital Where He Entered On Crutches
- 8 Suggestions to Keep the Immune System Strong in Ramadan
- Recovered From Thyroid Nodule with Needle Melting Method
- The Number of Completely Cured Cancer Types is Increasing Day by Day
- Pandemic Prevents Early Diagnosis of Glaucoma
- Misconceptions about Growth and Development in Children
- The Cause of Abdominal Pain Has Not Been Found for Years... Varicose Veins Appeared in Her Ovary
- Beware of hoarseness lasting longer than 15 days!
- While Cancer Occurrences Increase, Life Expectancy Also Increases
- Beware of Chocolate Cyst! It Affects 1 in 10 Women
- Chronic Renal Failure and Treatment
- Important Warning from the Expert: “Not Adding Salt to Meals Alone Is Not Enough”
- The Giant Stones In The Biliary Tract Of 71-Year-Old Patient Were Removed Without Surgery
- The American Cancer Society Has Announced; The Age of Screening For Lung Cancer Has Decreased
- Stress Triggers Thyroid Diseases; These Occupations Are At Risk!
- Causes of Male Factor Infertility
- Turkish Physician Developed a Novel Method for Parathyroid Transplant
- Survived Coronavirus, Had Windpipe Blockage Months Later, Returned From Death
- First Cartilage Transplant from a Donor
- The Effect of Advanced Age on IVF Treatment
- One Out Of Every Three People in Turkey is Pre-Diabetes
- Head Trauma Can Cause Permanent Damage
- Do Not Run Away From the Vaccine! The Coronavirus Itself Is More Dangerous Than The Side Effects of The Vaccine...
- Infertility
- 8 Tumors in the Large Intestine and Liver were Removed with a Single Surgery
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- Mosquito Infection Risk
- Early Menopause
- Blocked Fallopian Tube
- Vaginismus
- Sexual Dysfunction
- Low Ovarian Reserve (AMH)
- It is also Possible to Lose Weight During the Holidays!
- Which Methods Increase Success in Treatment of Infertility?
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
- Microinjection
- Egg Cryopreservation
- Assisted Hatching
- Summer Recipes
- Micro-chip
- Are Vaccines Effective Against Delta Plus?
- Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis
- Tips for Potty Training…
- The Father Beat Hepatitis B and Cirrhosis with the Liver From His Daughter and Beat The Cancer
- Immune Enhancing Nutrients
- Holiday Guide for Families with Children
- Thyroid Diseases During Pregnancy Affect the Baby as Much as the Mother
- 8 Mistakes That Make Weight Loss Harder
- ‘Hand, foot, mouth disease’ Warning from the specialist of the subject: "It is more Common in Children Going to the Pool in Summer!”
- Experts Warn: In Case of Fainting, Consult a Cardiologist First
- Urinary Tract Infections Can Be A Sign Of Menopause
- Hidden Lung Cancer Cases Revealed in Tomographs Taken Due to Coronavirus
- Allergic Disease Rates Increased from 3% to 15% in the Last 20 Years
- Why aren’t Antibiotics Working Any More?
- Causes of Arhythmia Can be Displayed in 3D
- Don’t Let Allergic Rhinitis Spoil Your Life
- What Should be Paid Attention to in Face-to-Face Education?
- Sleep Apnea
- Sepsis Costs the Life of One Person Every 2.8 Seconds!
- Epidurals Sorting Fact From Fiction!
- Healthy Microbiota Reduces the Risk of Alzheimer's
- Being Young Does Not Protect From Heart Disease!
- Don’t Risk Your Brain!
- What Should Be Considered After Parathyroid Surgery?
- It is Vital to Act Quickly in Case of a Heart Attack
- Skipping Mammography Screening Can Be a Life-Threatening Risk!
- 8 People a Day Lose Their Lives While Waiting for Organ Transplantation in Our Country
- 10 Overlooked Signs of Menopause
- Emotional Stress May Affect Risk of Recurrence in Breast Cancer
- 648 Grams Born Baby “Umut” Succeeded in Clinging to Life
- The World Raises an “Alarm” on Antibiotic Resistance!
- The Hope of ‘Immunotherapy’ in Advanced-Stage Cancer Treatment
- Quitting Smoking Even After Diagnosing Lung Cancer Effects Lifespan
- Endometriosis
- Thought Stomach Ulcer; Pancreatic Cancer Caught in the First Stage
- A Common But Little-Known Disease: Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
- Electronic Cigarettes Can Cause Heart Attacks!
- Pay Attention to the Pain That Occurs in the Front Part of Your Knees While Playing Sports!
- Attention to Drug Use After Kidney Transplantation!
- Does Prostate Enlargement Develop into Cancer?
- Healthy New Year's Eve Table Suggestions
- High Fever in Children Article Series I
- High Fever in Children Article Series II
- One in Every Four Men Diagnosed with Cancer Has Prostate Cancer
- Ways to Protect Prostate Health
- Surgical Treatment of Prostate Diseases
- Ways to Get Rid of Kidney Stones
- Prostate Preventive Cancer Treatment: Focal HIFU
- HIFU Focal Treatment for Prostate Cancer
- The Things You Should Know About Prostate Cancer
- HoLEP Method in Closed Prostate Surgery
- Benign Prostate Enlargement
- High Fever in Children Article Series III
- High Fever in Children Article Series IV
- Co-Culture
- Rhinoplasty
- High Fever in Children Article Series V
- Ovarian Rejuvenation / PRP
- Parathyroid Diseases and Treatment
- They Said It Was Thyroid Cancer, But It Turned Out to Be Parathyroid Adenoma!
- The Process That Leads to Kidney Failure in Young People Progresses Sneakily
- Although Her Fears Prevented Her from Going to the Hospital, She Managed to Beat Breast Cancer at the Age of 70
- As Average Life Expectancy Increases, This Problem Will Be Seen More
- Do I Have Covid or Influenza?
- Why Does Omicron Increase in Children?
- What is COVID-19?
- Weather Change Triggers Migraine Attacks
- Cancer Statistics Reveal the Importance of Protecting Against Cancer
- Skin Microbiota May Affect Immunity!
- The Mask Requirement was Removed and the Importance of Social Distance Increased!
- 'Early Age' Warning for Egg Freezing Procedure
- New Research Points to the Important Issues in Breast Cancer
- What is Acromegaly Disease?
- The Amount of Nutrients Needed for Satiety Decreases as Eating Time Increases!
- Covid-19 Pandemic Created a New Diabetes Type!
- Age of Breast Cancer Prevalence Falls, yet Mortality Declines
- 8 Common Misconceptions About Sports Injuries
- Found Out That She Had Cancer After Her Accident, and Immunotherapy Was Her Solution!
- Beware, These Risks Increase After Menopause!
- Patients with Refractory Epilepsy May Lose Time Until They Receive a Proper Diagnosis
- Pollen Allergy Has No Season
- Beware of Little-Known Risks of Smoking!
- Obesity is Both a Cause and Consequence of Sleep Apnea
- Health Problems Triggered After Recovery from Covid
- This Problem Ruins the Lives of One in Every 10 Women
- The Young Man Whose Trachea Was Completely Blocked After An Accident Regained Both His Health and His Voice
- Check-ups Following the Vacations!
- The Frequency of Thyroid Nodules and Thyroid Cancer in Young People is Increasing!
- Methods to Deal with Bad Cholesterol
- Getting Cancer Treatment Does Not Stop You from Having Children!
- Fetal Anomalies in Consanguineous Marriages Can Be Diagnosed in the Womb
- Do not take unneeded calories to your body
- How to Prevent COVID-19 in School-Going Children
- Interventional Methods in the Treatment of Acute Stroke
- Breast MRI
- Breast Ultrasound
- Thyroid Cancer Treatment Is Possible Without Removing The Entire Thyroid Gland
- Mammography
- Sensitivity of Breast Tomosynthesis is Higher in the Young Population
- Breast Radiology
- Your Real Age Is Your Vascular Age
- Breast Cancer Screening Applications Decreased by 10% Before the Pandemic
- Prof. Dr. Attar: Endometriosis Can Be Associated With Some Chronic Diseases
- Side Effects of Chemotherapy and Coping Methods
- How Is Stomach Infection Transmitted?
- Life Support Booklet for Oncology Patients
- Hot Chemotherapy (HIPEC)
- 9 Different Types of Depression
- Young Patient Who Could Not Walk Due to Cartilage Damage Recovered With Cartilage Transplantation
- Facts About Breast Cancer
- Asthma and COPD Attack Season Begins
- You May Have Leptin Resistance Below Your Constant Desire To Eat!
- Piriformis Syndrome May Be the Cause of Low Back Pain and Numbness in the Legs
- Flu Is Widely Seen This Year
- WHO (World Health Organization) Warns for Antibiotic Resistance!
- Foods That Increase Blood Sugar
- Father's Role in Child Development is Fatal
- The Nutritional Principle of the Feast of Sacrifice Should Be Balance
- Attention! Holiday Return Cases May Increase
- Caffeine Consumption in Children
- Who Is Threatened by Monkeypox?
- Hot Shock in Children
- Recovery from SMA Depends on the Carrier Testing
- What Is the Period of Fertility? What Tests are Performed for Fertility?
- Dumping Syndrome
- Seborrheic Dermatitis, Commonly Called Milk Crust, or Eczema
- Akrep Sokması
- Safe Use of Herbal Medicines Before Anesthesia
- Are Your Kidneys Really Healthy?
- Symptoms of Bone Marrow Cancer
- Why Do Mosquitoes Bite Some People More?
- What is Agoraphobia?
- How Effective Are Vaccines Against New Variants?
- Endometrial Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Genetics is the Key Cause of Food Allergies in Children
- Not Every Sore Throat Is Caused by an Infection!
- External Genital Area (Vulva) Cancer
- Gynecological Cancers
- Being Thirsty in the Heat Tires the Kidneys!
- Suggestions to Increase Metabolic Rate…
- Why Is Vitamin D Deficiency So Common in Türkiye?
- Use of Vitamin D in Pregnant Women
- Notice the Dangers in the School Bag!
- Pay Attention to Food Allergies in Children!
- Use of Vitamin D in Children
- Thyroid Storm
- How Should the Development of a Baby Be?
- T4 Hormone in 13 Headings
- KaryoBaby | Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
- Questions About Thyroid Diseases
- Liver Cancer (Tumor) and Treatment
- What Is a Fracture and How Is It Treated?
- Strabismus and its Treatment
- Pay Attention to the Flashing Light in the Eye!
- Urinary Incontinence
- Burnout Syndrome
- Suffering from Insomnia?
- What is Intubation?
- Nutritional Guide to Strengthen Immunity
- The Right Behaviors to Shape the Pandemic
- Ways to Survive Coronavirus Stress
- Do Not Be Overly Anxious and Panicky with Children
- Liver Transplant Clinic Patient Education and Home Care
- Acne and Diet
- Neurological Problems and Coronavirus
- Tissue Harmony Is Also Important for Success in Kidney Transplant
- Nutrition Recommendations Before the Exam
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- False Facts in Cancer
- How to Feed Children in Summer?
- Can Cervical Cancer Be Prevented in Women?
- Is There a Nutritional Difference Between Sports to Increase BMI and Sports to Lose Weight?
- Swine Flu / H1N1
- What Should You Do to Avoid Gaining Weight for the Holidays? Do Not Be a Victim of the Buffet
- Read This Before You Travel!
- The Order Of The Children Starting School Should Be Changed
- Knee Arthritis
- Stem Cell Therapy in Orthopedic Diseases
- Thyroid Diseases
- 3-Dimensional Diagnostic Method in Breast Tumors: TOMOSYNTHESIS
- Zika Virus Poses The Greatest Threat To Expectant Mothers
- Considerations for Embryo Transfer
- What Causes Menstrual Irregularity, How Is It Treated?
- What is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
- Goiter (Thyroid Gland) Biopsy
- Success in IVF after 43 Decreases to Five Percent
- Interventional Radiology is Used in Many Fields
- Do Not Immediately Take Antibiotics for Colds and Flu
- Cold Weather May Affect Facial Nerves, Increasing the Risk of Facial Palsy
- Epilepsy
- Aspirin Used Without Physician's Advice Increases Risk of Bleeding!
- Do Not Unconsciously Turn to Herbal Products to Get Rid of Winter Fatigue
- Treatment of Swallowing Disorders
- What is Psychoneurosis?
- Capsule Endoscopy
- Which Vaccine Should Be Given to Adults and When?
- Aging Begins in the 20s
- Diabetes Mellitus and its Treatment
- Radiofrequency Therapy in Thyroid Nodules
- What are the Symptoms of Flu? What is Good for Flu? How Does Flu Goes Away?
- Stretta / Endoscopic Reflux Treatment
- Fundoplication Method / Endoscopic Reflux Treatment
- Experts Do not Recommend Food Sensitivity Tests
- Throat Reflux
- Blood Pressure Holter
- Hypophysis Clinic
- Guidelines for Safe Living After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Techniques and Applications Used in Gastroenterology
- 60 - 70 Percent of Liver Cancer and Liver Transplantations Is Due to Chronic Hepatitis
- What is Lymphedema?
- Swimmer's Ear is A Summer Illness; Beware!
- What is Sepsis?
- Music Therapy
- Cancer and Exercise
- Curiosities About Breast Cancer
- Osteopathy
- The Way to Peace: Yoga
- Cancer and Nutrition
- Coronary CT Angiography (Virtual Angiography)
- Nutrition and Diet
- Dancing with Cancer
- Life Returns to Normal with Caution
- Rules to be Followed in Shopping Malls
- Lung Cancer
- COVID-19 Vaccination in Children
- Who Can Undergo HoLEP Procedure?
- What is MS Disease (Multiple Sclerosis)?
- Complementary Foods for Babies
- Omicron Variant
- Gallbladder Stones
- Thyroid Biopsy
- High Fever in Children
- Childhood Obesity and Nutritional Recommendations
- Most Common Cancers
- What is Aphasia?
- Effort Test
- Biopsy for Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors
- What is Type-2 Diabetes?
- Blood Glucose Measurement
- Check Up for Females Over 40
- Check Up for Females Under 40
- Check Up for Females Over 50
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Check Up for Males Under 40
- Check Up for Males Over 40
- Bone Metastasis
- Check Up for Males Over 50
- Cardiology Check-Up
- Child Check-Up
- Child Check Up Package
- Psychologist Package
- Dietitian Package
- 10 Tips for Diet on Religious Holidays
- What is Specific Learning Disability?
- 5-Day Recovery Diet After the Religious Holidays
- What is a Mental Disability?
- What is Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder?
- Developmental Disorders in Children
- Treatment of Pituitary Adenomas
- Surgical Treatment of Pituitary Diseases
- Pituitary Clinic | FAQs
- What Diseases Is Interventional Radiology Used For?
- Phytotherapy and Immune System
- Important Warning from The Expert: “Not Every Large Tumor is Advanced Cancer”
- Phytotherapy
- Mental Health Starts in the Family
- Healthy Diet
- Check Up Packs
- What to Do for Influenza That Does not Recover?
- What is Autism?
- Knee Pain
- Thyroid-Related Eye Diseases
- Glaucoma
- Pain Treatment
- What Is Autoimmune Hypoparathyroidism or Hypocalcemia?
- What Is The Loss of Low Calcium Level in Blood?
- What Is The Symptoms of Calcium Level Elevation (Hypercalcemia)?
- How It Is Made The Parathyroid Adenoma Operation?
- What Is Parathyroid Hyperplasia?
- Parathyroid Tumors
- What Are The Parathyroid Glands?
- Liver Diseases
- Who Can Be A Donor For Liver Transplant?
- Who Cannot Be A Donor For Liver Transplant
- Liver Transplant Recipient And Donor Preparation
- Macular Degeneration (Yellow Spot)
- One in Three People Has Pre-Diabetes
- Spinal Cord and Spine Tumors
- Healthy Aging Course
- Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment
- 5 Causes of Constantly Feeling Cold
- Molecular Imaging and Treatment in Prostate Cancer
- Lutetium Treatment in Neuroendocrine Tumors
- How Should I Dress My Baby?
- Points to Be Considered in Baby Clothing
- 7 Things You Should Know About SIBO Disease
- How Should Home Care Be After a Liver Transplant?
- What is Monkeypox Virus? What Are the Symptoms of the Monkeypox Virus?
- Liver Transplant Vocabulary
- Causes and Treatment of Obesity in Children
- Snake Bites
- Snoring and Its Treatment
- Sunburn
- How to Protect Yourself from Sunburn?
- Throat Infection
- ENT Problems Seen in the Summer
- Nose Bleeding
- What is Lyme Disease?
- Common Misconceptions About Cancer
- How to Drink Water: Warm, Cold, or Hot?
- Liver Transplant - Frequently Asked Questions
- Elderly Care
- Heart Attack Causes and Symptoms
- Choosing Summer Clothes for Kids and Babies
- What Should a Family with Children Have in Their Summer Suitcase?
- Liver Transplant
- How to Feed Newborn Babies and Toddlers in the Summer?
- Migraine and Its Treatment
- Symptoms and Treatment of Sepsis
- Pregnancy Cholestasis
- How to Swallow the Drug?
- What and How Much Should Children Eat at Which Time of Meal?
- How to Apply for Bone Marrow Transplant?
- What is the Right Lunch Box for Children?
- Adult Bone Marrow Transplant / Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Bone Marrow Transplant?
- Bone Marrow Transplant Clinic
- What are Hematopoietic Stem Cells and What is Their Function?
- How to Apply for Bone Marrow Transplantation?
- Frequently Asked Questions in Hematopoietic Stem Cell / Bone Marrow Transplantation
- What is a Brain Aneurysm?
- Protecting Children from COVID-19
- Alkaline Nutrition
- What Is Appendicitis?
- How Many Days Do the Side Effects of the Pneumonia Vaccine Last?
- How to Tell if You Have a Mild Coronavirus?
- Safe Shopping Rules for Protection from Coronavirus
- One of the Most Effective Weapons Against Coronavirus Is a Strong Immune System
- Pay Attention to These Rules for COVID-19
- 9 Tips to Prevent You from Gaining Weight While at Home
- Is it Necessary to Disinfect Outdoors?
- Hygiene in the Shopping for Kitchen
- Can the Coronavirus Be Transmitted Through What We Eat?
- Hand Sanitizer Usage Guide
- Masks and Gloves Thrown Onto the Street Pose Danger
- What is a Kidney Transplant?
- Use of Gloves During the Pandemic
- How Should We Clean Mobile Phones?
- Not Having a Fever Does Not Mean ‘There Is No Infection’
- Common Misconceptions About Coronavirus
- Frequently Asked Questions About Coronavirus
- Catching Coronavirus
- Does Pregnant Coronaviruses Affect?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Coronavirus
- Does the Pneumonia Vaccine Protect Against the Coronavirus?
- Why Are the Elderly at Risk for Coronavirus?
- Multiple Tests Are Available for COVID-19
- Who Should Be Vaccinated Against Pneumonia?
- Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
- Psoriasis
- Hemorrhoid Treatment
- Nutrition in Celiac Disease
- Interventional Oncology
- Most Frequently Asked Questions During Pregnancy
- General Intensive Care Unit
- What is Language and Speech Disorders?
- What are Pituitary Diseases?
- What is the Pituitary Gland, What are its Functions?
- Questions About Gastroenterology Surgery
- What is Hirsutism?
- Hirsutism Clinic / FAQs
- What İs Profile Aesthetics?
- Waist, Hip and Leg Aesthetics
- Turkish Doctors Saved the Finger Said To Be Amputated In Germany and Bulgaria
- Prepare Your Skin For Summer
- Diabetic Patients Should Not Wear New Shoes for More Than 2 Hours
- Non-Surgical Rhinoplasty Can Be Performed With Fillers
- Returning to Exercising After Aesthetic Operation
- Prominent Ear (Otoplasty)
- Facial Sagging and Tired Look Can Be Eliminated After Weight Loss
- What are Medical Aesthetic Applications?
- There Are Satisfactory Results in The Treatment of Canine Mammary Disease
- Liposuction
- Breast Enlargement
- Breast Lift
- Breast Aesthetics FAQ
- Breast Aesthetics
- Breast Reduction
- Surgery for Breast Cancer and Breast Aesthetics Can Be Performed Simultaneously
- Plastic Surgery Does Not Just Serve Aesthetics
- Turkish Doctor's New Method in Breast Reduction for the Elderly
- Now He Can Run Freely Thanks to the Surgery Performed in Turkey
- Body Contouring Surgery
- Beware of New Moles and Non-Healing Wounds
- Aesthetic Solutions for Tired Eyes
- Face Lift Surgery
- They Set Out Together For Their Dreams
- What are the Types of Obesity Surgeries?
- Questions About Obesity Surgery
- A New Era in Obesity Surgery
- Overweight
- If You Have Diabetes, Consult An Ophthalmologist At Least Once A Year.
- Long-term Computer Use Pose a Threat to Eye Health
- It was Told that She could Lose Both Eyes, but She Recovered with an Operation
- Untreated Strabismus Can Cause Vision Problems!
- The Danger to the World: MYOPIA
- Eyelid Diseases
- Is Strabismus Genetic?
- One in 20 Newborns Have Tear Duct Obstruction
- Eyes May be Affected During Pregnancy
- Are Flies Flying Before Your Eyes?
- 7 Tips to Protect Your Eye Health
- About Half of Glaucoma Patients Are Unaware of Their Disease
- Allergic Conjunctivitis (Eye Allergy)
- Brain Battery Connecting Parkinson Patients to Life
- Pain in the Legs May Be a Sign of Vascular Congestion
- Which Diseases Can Swelling in the Legs Indicate?
- Stay Away from Depression and Protect Your Heart!
- Do Not Let Varicose Veins Be Your Nightmare During Pregnancy!
- Frequently Asked Questions About Varicose Vein
- Treatment Success in Brain Tumors Also Depends on the Family
- Not All Hand Tremors Are Caused by the Parkinson's Disease
- Do not Fill Your Brain With Junk Food If You Want A Good Memory
- Numbness in the Arms Can Be A Sign of Neck Hernia
- When Does the Spine Require Surgical Treatment?
- Osteoporotic Spinal Fractures Can Cause Bigger Problems If Not Treated Early
- Patient Selection is Important in Parkinson's Surgery
- Canal Narrowing in the Spinal Cord
- Beware If Your Walking Distance Is Decreasing!
- 6 Problems Causing Pain in the Feet
- Due to His Weight, He Could Not Take Care of His Children; He Lost 57 Kilograms and Regained His Health
- Are Obesity Surgeries Risky?
- 60 Percent of Shoulder Pain Complaints are Caused by Shoulder Impingement
- Meniscus Tear Warning from a Specialist: Beware of Sports Grounds!
- Targeted Atomic Therapy is Hope for Many Cancers
- Crunching in the Kneecap May Be a Sign of Calcification
- Untreated Genital Problems Can Cause Urinary Incontinence
- Can Permanent Treatment Be Provided for Rhythm Disorders?
- Attention to the Genetic and Nutritional Factor: Five Out of Every 100 Children Have a Kidney Stone Problem
- Pregnancy Helps Reduce the Risk of Uterine Cancer
- Protective Equipment Required When Using Electric Scooters
- Obesity Increases Early Puberty
- Injured Athletes Can Return To Sports With Cartilage Transplant
- 9 Suggestions to Fix Childrens Deteriorated Eating Habits
- Varicose Veins Treatment Using Sclerotherapy
- Goal in Heart Diseases; To reduce the loss of life by at least 25 percent by 2025
- The Incidence of Thyroid Cancer Has Increased! There is Turkey in the Research!
- Breastfed Babies Have Lower Blood Pressure, and Their Hearts are Healthier
- Infection Can Cause the Onset of Asthma Disease
- New Study Surprised: “Mortality Increased in Breast Cancer Cases Under the Age of 40”
- New Treatment Approaches Promising in Metastatic Breast Cancer
- Pay Attention To The Child Who Snores At Least 3 Days A Week!
- If You Have Abdominal Pain At Least Once A Week, Beware!
- Pay Attention to the Temporary Complaints of MS!
- Eco-Anxiety Can Cause Panic Attacks
- Gold Standard Treatment for Benign Prostate Enlargement: HoLEP
- Thyroid Hormone Deficiency May Cause Short Stature
- 1 in 10 Women Have This Problem; It Can Lead To Infertility
- Technique Developed by a Turkish Doctor Has Become Part of Literature; Is Now an Alternative to Pacemakers
- Unexpected Causes of Hearing Loss
- Hernias in Children Should Be Intervented Without Wasting Time
- Effective Results Can Be Achieved with PRP in Women with Low Egg Count
- Key Surgery Performed In Turkish Hospital For First Time
- Hereditary Kidney Diseases Are Underrecognized!
- 6 Misconceptions About Kidney Stones
- What to do from Iftar to Sahur for a Healthy Ramadan
- Treatment of Knee Arthrosis Varies According to the Person
- 9 Tips for Proper Nutrition During Pregnancy
- A Lack of Attention to Sports Injuries in Children May Affect Their Development
- The Priority Rule for the Protection from Summer Infections is Hygiene
- Misconceptions about Cholesterol!
- Necessary Precautions to Protect Children from the Harmful Effects of the Sun
- Professors from America Came to Watch the Technique Developed by the Turkish Physician on Site!
- Constant Feeling of Hunger Might Actually be Hiding Some Diseases!
- The First One Hour Saves Lives in Sepsis
- In Case You Are Unable To Sleep Even If You Are Tired, Your Circadian Rhythm May Be Disrupted
- Insidious Danger of Pathological Fractures Increase in Recent Years
- Using Antipyretics Uncontrolled Can Hide Pneumonia Symptoms
- Beware of Infections in Schoolchildren
- Does Environmental Pollution Cause an Increase in the Cases of the Hypospadias?
- Age Well With the Magic of Herbs, Veggies, Fruits
- Walking Problems of Children Might Indicate Vertigo
- Her Kidney Stone, 6 cm in Size, Was Taken With One And a Half Hour Operation
- Non-Surgical Reflux Treatment
- Eye Problems Increase as Children's Digital Screen Time Extends
Alo Yeditepe